Diabetes is a chronic disease that causes unhealthy amounts of sugar in the bloodstream. This occurs because of one of two reasons. First, the pancreas does not produce enough insulin – which is the hormone in charge of regulating blood glucose. Second, the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces.
Did you know that according to the latest figures, 11% of Indians are diabetic and around 15% are pre-diabetic? With 101 million people affected, India is now considered the diabetic capital of the world. The main culprits are unhealthy diets, lack of physical activity as well as the harmful use of alcohol and tobacco.
Given these numbers, it is safe to say that we are experiencing a diabetes epidemic, which begs the questions: is it preventable or reversible? how can it be managed?
Different types of diabetes
To begin, it’s important to distinguish between three main types of diabetes, however there exist many more:
- Type 1 affects 98.000 individuals in India, it develops rapidly, and is typically diagnosed in children, teenagers, and young adults.
- Type 2 affects 7 out of 100 individuals with diabetes, it develops gradually over time, and is generally diagnosed in adults.
- Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy with a prevalence of 1.3%.
Type 1 is caused by an autoimmune reaction whereby the body attacks itself by mistake. This reaction destroys the pancreatic cells that produce insulin.
What causes the autoimmune reaction is a combination of genetic traits transmitted from parent to child and environmental triggers, such as a virus. However, not everyone with genetic predisposition develops type 1 diabetes.
Moreover, as opposed to other types of diabetes, diet and lifestyle choices do not cause type 1 diabetes.
Type 2 arises when pancreatic cells don’t respond normally to insulin. This phenomenon is called insulin resistance and triggers the pancreas to produce increasingly more insulin. On the long run, blood sugar rises, setting the stage for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes.
While the causes of type 2 diabetes are not fully known, obesity, physical inactivity, high blood pressure and high cholesterol are well known risk factors. This means that type 2 diabetes is largely preventable through lifestyle changes like maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, avoiding smoking, and limiting alcohol intake. These steps can significantly reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, particularly in individuals with predisposing factors like obesity or a family history of the disease.
Early detection and intervention can also help prevent or delay the onset of complications associated with diabetes.
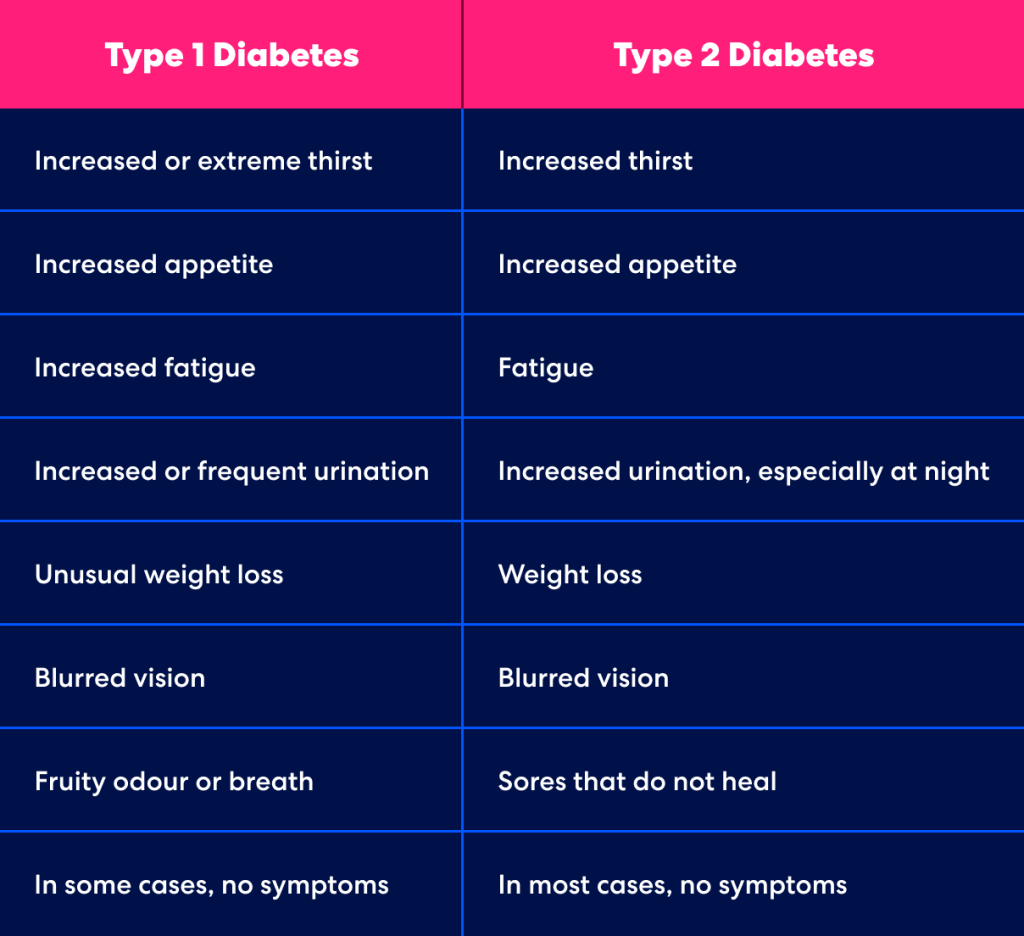
Recognise the symptoms.
Is diabetes reversible?
This is one of the most pressing questions asked by our members. Unfortunately, the short answer is no. But though it cannot be cured, it can be managed successfully.
Some people are able to control their diabetes by eating a balanced diet, maintaining a healthy body weight, and exercising regularly. Many individuals, however, must take oral medication and/or administer insulin injections to keep blood sugar levels under control.
Diagnosed with diabetes – what’s next?
In case you tested positive for diabetes or at risk of developing type 2 diabetes, the doctor is likely to prescribe you:
- A pharmaceutical therapy,
- Lifestyle changes, and
- Follow up check up within 3 months

Managing Diabetes Effectively
Individuals working conventional nine-to-five jobs can encounter extra challenges in maintaining dietary and exercise regimens to keep their blood sugar within a healthy range.
Some occupational factors that can affect diabetes management, include:
- Working long or irregular hours that make it difficult to follow a healthy diet and exercise regularly.
- Cortisol levels, or stress, can raise blood sugar levels and make it difficult to manage diabetes.
- Jobs that require heavy lifting or other strenuous physical activity.
- Frequent travel or long commutes that can make maintaining consistent blood sugar control challenging.
Managing diabetes demands continuous attention to blood sugar levels, even when you are soaked in work and chasing urgent deadlines.
Even’s success.
Among Even’s members who participated in the diabetes management programme, we recorded the following positive trends:
- Average HbA1c reduction of 1.7
- 5kg weight loss in 3 months
- 100% of the cohort felt an increase in understanding of how to manage diabetes better in everyday life
How can you stay on track?
Download the Even app and stay in touch with your Even doctor – we take care of the rest!